Teilprojekt (TP) 13
Project partner: Dr. Heike Bach, VISTA Geowissenschaftliche Fernerkundung GmbH
TP-Title:
Canopy status assesment using remote sensing for
model based yield estimation
TP
short title: Model based analyses with remote sensing
TP-aim:
Application of hyperspectral remote sensing data,
respectively their coupling with model simulations for the description of
canopy status and yield estimation on heterogeneous surfaces. The results shall
serve as basis for the decision making process in precision farming.
Status
of the TP combination: Thematical cooperation with
TP 4, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 22 and 23. Provision of canopy information of the
test fields for the project partners.
Short description
The
aim of subproject 13 will be the model based analysis of remote sensing data of
an imaging spectrometer to retrieve canopy
status on the pilot farms of the cooperative project. The imaging spectrometer
AVIS (Airborne Visible Infrared Imaging Spectrometer) will acquire
multitemporal datasets with a high spatial resolution (2-4m) to monitor the
reflectance of the canopies (approx. 4 acquisitions per vegetation period). Furthermore
the ESA will provide remote sensing data of the hyperspectral directional
imaging spectrometer CHRIS.
Canopy
parameters will be derived on the basis of spectral measurements alone. In
addition, the radiation transfer model SLC, an enhancement of GeoSAIL (Verhoef &
Bach, 2003), will be applied for simulation of the canopy reflectance. This
model aided analysis allows for quantitative analyses and regional
transferability of the results. Comparison between the retrieved canopy
parameters and other methods of gathering the surface information (e.g. Yara-
and Pendel sensor and the results of on-field optical sensors) will be drawn. Accuracy
assessment on the basis of the field measurements on the pilot farms will be
conducted for validation purposes.
In
a second step of model supported analyses, an assessment of the information
acquisition through coupling of remote sensing information with meteorological
data, soil information and a plant growth model will be developed. Through
gradual adaptation of the canopy parameters (e.g. leaf area and plant density)
the modelled reflectance values for each pixel are fitted to the measured values.
Thus a calibrated spatial distribution of plant parameters as an improved input for the model is determined.
The
results will be used for yield estimation and as the basis for the decision making process in precision farming. The first two years of investigation
are reserved for method development. A test application and a test of the
transferability to larger areas will follow in year 3.
Status Quo
Three
aerial flights will be conducted with the imaging spectrometer AVIS in 2005.
Acquisition planning is in progress. The acquisitions will be adapted to the
2005 field selection and the desired spatial resolution in each of the two
investigation areas.
Wimex
has already been established as a CHRIS test site of ESA last year, Groß
Twülpstedt is added as a test-site in 2005. Some CHRIS scenes of 2004 are existing for Wimex. A clear cloud scene of Sep 9 2004 was
corrected for radiometric and atmospheric errors. As result spectral reflectance
values were derived, which describe the absorption and reflectance of the land
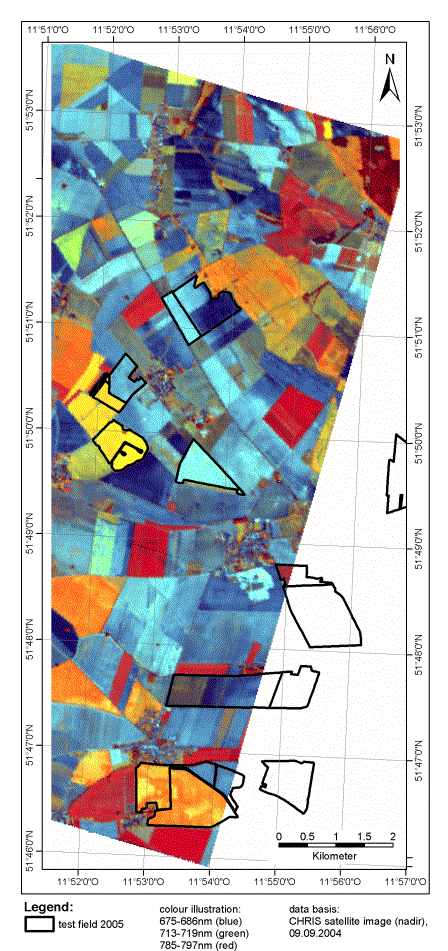
surface. As CHRIS is a multiangular
imaging spectrometer, scenes are available at different observation angles. A
geometrical correction was performed on some of the angular scenes. The
following illustration shows the Sep 9th nadir scene overlaid with the test
fields of 2005. The analyses of the data will take place in the coming
investigation period.
Also
the development of the canopy radiation model SLC, which provides a method for
extraction of canopy parameters from hyperspectral data, will continue.
Substantial questions:
·
Is the
application of hyperspectral remote sensing data using AVIS suitable for
decision making in precision farming?
·
How
accurate are model simulations based on remote sensing for the description of
current canopy status and yield estimation
on heterogeneous surfaces?
·
Are
the results of Yara- and Pendelsensor
and of on-field optical sensors comparable to the results attained on the basis
of hyperspectral data?
·
Which
possibilities offers the model aided analysis of remote sensing data in regard
to plant protection?
·
Are
the retrieved yield data of the subarea transferable to a larger area, so that
a regionally transferable modelling method is obtained?
Date of issue: 08.04.2005